At the Hot Chips 2024 semiconductor conference, Intel has covered 4 major grounds for its upcoming releases so let’s find out what is up about them.
Intel Xeon 6 SoC
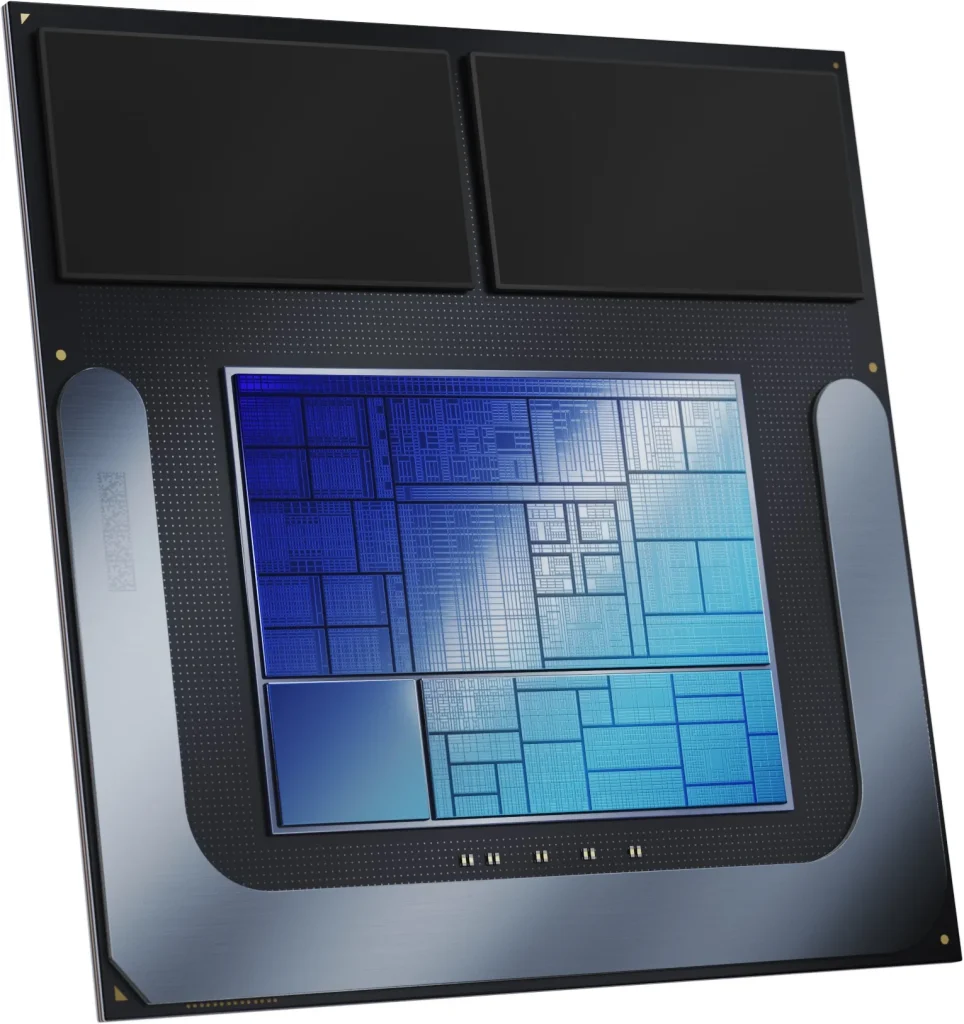
Slightly mentioned during MWC 2024, the Intel “Granite Rapids-D” processor is now officially known as the Xeon 6 SoC designed for edge computing related to AI and scalar workloads that also maintain a strong level of connectivity. As the latest generation of processors, these are made for applications with certain restrictions and constraints related to deployment space and power budget so that extreme environments can also take advantage of them.
According to Intel, they are using the Intel-3-made Xeon 6 as the base and integrating another Intel 4-fabricated I/O chipset optimized for edge to deliver large improvements in performance, power efficiency, and transistor density. Specifically, the entire structure uses a unified cache and memory through a mesh superhighway interconnect for reduced latency and jitter.
Here’s a quick summary of some of the important key points about Xeon 6 SoC:
- P-Core based on Redwood Cove
- Quad/Octa-channel RAM support (DDR5-5600 & MCR-DIMM)
- 32 PCIe 5.0 / 16 PCIe 4.0 / 16 CXL 2.0 lanes
- Max 8x Ethernet Ports of 4x 50G and 2x 100G
Notable features also include new media acceleration capabilities designed for better video transcode and analytics for live OTT, VOD, and broadcast media, Advanced Vector Extensions and Advanced Matrix Extensions dedicated for inferencing, QuickAssist Technology for higher efficiency in network and storage performance; vRAN Boost that optimizes power curves for virtual RAN, and the Tiber Edge Platform that streamlines the “build, deploy, manage, scale” process for edge and AI solutions on standard hardware.
Early talks for Lunar Lake Processor and Gaudi 3 AI Accelerator
Slated for next week’s official launch, Intel did teased a bit about the next-gen Intel Core Ultra processors codenamed Lunar Lake tested and proven to be the best x86 processor in terms of core, graphics, and client AI performance with its new P-cores and E-cores architecture enabling higher performance while keeping power consumption in check with up to 40% less. Meanwhile, the NPU is up to 4x faster which accelerates currently available gen-AI models at a much quicker rate while enabling more powerful ones in the future. And of course, we can’t forget about the Xe2 GPU bringing up to 50% more gaming and graphics performance than last gen.
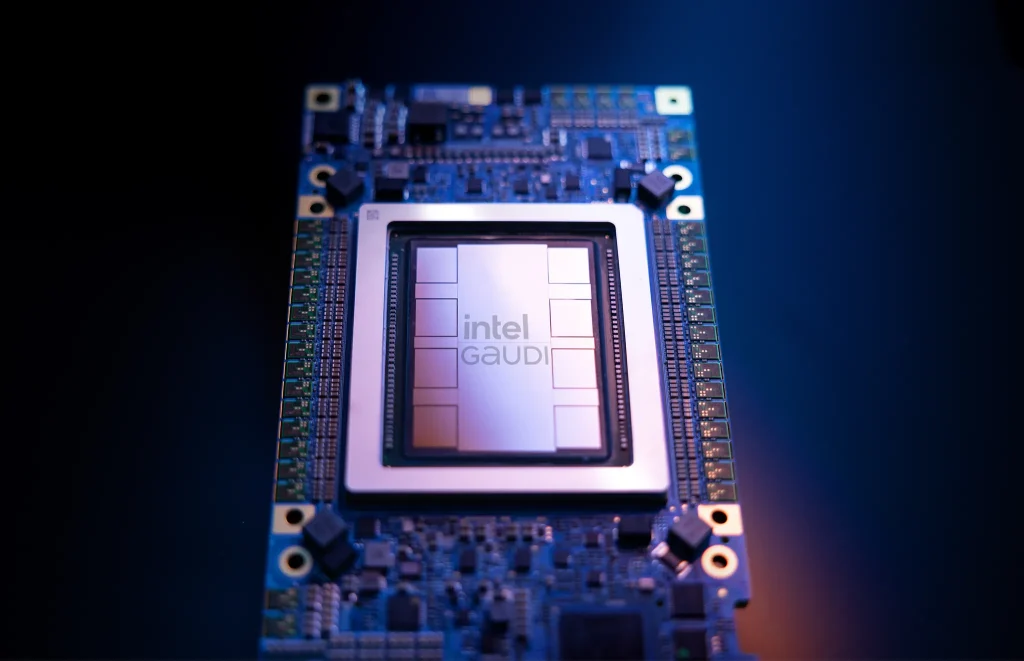
The same thing can be said for Gaudi 3 as well despite the official reveal still at TBA at the moment. Surface details revealed that it is using an optimized architecture that targets compute, memory, and networking as well as efficient matrix multiplication engines to go with a 2-level cache integration and extensive RoCE (RDMA over Converged Ethernet) networking, resulting in a cost-effective and power-efficient AI data center.
Lastly, Intel also showcased the new Optical Compute Interconnect (OCI) chipset that is co-packaged with an Intel CPU designed with 64-channel 32Gbps data transmission in each direction of fibre optics of up to 100 meters which can really impact the AI infrastructure’s growing demand for ever higher bandwidth, longer reach, and reduced power consumption.