AMD has finally unleashed the Ryzen 9 9900X and 9950X, aiming to redefine high-performance computing. These flagship processors feature the refined Zen 5 architecture, designed to excel in both single-core and multi-threaded tasks. Whether you’re a demanding content creator, a passionate gamer, or a productivity-driven professional, these CPUs promise exceptional performance.
In this review, we’ll thoroughly test these chips to see if they truly live up to the hype and can claim the high-performance crown, challenging their predecessors and the current top contender from Intel, the Core i9-14900K.
Specifications
| SKU | Cores / Threads | Base / Boost Clock | L2 Cache | L3 Cache | TDP | Price (USD) |
| Ryzen 9 9900X | 12C/24T | 4.4GHz / 5.6GHz | 12MB | 64MB | 120W | $499 |
| Ryzen 9 9950X | 16C/32T | 4.3GHz / 5.7GHz | 16MB | 64MB | 170W | $649 |
Overview
This slideshow requires JavaScript.
In terms of packaging, the Ryzen 9 9900X and 9950X come in a simpler package than their predecessor, though they do not include a box cooler. AMD has followed Intel’s approach with the Ryzen 9000 lineup, omitting the box cooler since most users prefer third-party solutions.
However, we still hope AMD will consider including the Wraith Prism cooler with its Ryzen 9 desktop CPUs, given its capabilities. With the Eco mode available in the BIOS, there’s a strong case for including a box cooler, as it would be appealing for users who want to leverage Eco mode in small form factor builds.
Test system list
Before diving into the benchmark results, let’s outline the components used in our Intel and AMD test systems:
Test System 1
| CPU | Intel Core i9-14900K |
| Motherboard | ASUS ROG Maximus Z790 APEX Encore |
| Memory | G.Skill Trident Z5 DDR5-6000 CL30 (16GB x2) |
| Graphics Card | GeForce RTX 3080 10G |
| Power Supply | Cooler Master M2000 Platinum 2000W |
| Primary Storage | Kingston KC3000 2TB |
| Secondary Storage | PNY XLR8 CS3040 2TB |
| CPU Cooler | Cooler Master MasterLiquid PL360 Flux |
| Chassis | Streacom Open BenchTable |
Test System 2
| CPU | AMD Ryzen 9 7900X / AMD Ryzen 9 7950X /AMD Ryzen 9 9900X / AMD Ryzen 9 9950X |
| Motherboard | ASUS ROG Crosshair X670E Hero |
| Memory | G.Skill Trident Z5 DDR5-6000 CL30 (16GB x2) |
| Graphics Card | GeForce RTX 3080 10G |
| Power Supply | Cooler Master M2000 Platinum 2000W |
| Primary Storage | Kingston KC3000 2TB |
| Secondary Storage | PNY XLR8 CS3040 2TB |
| CPU Cooler | Cooler Master MasterLiquid PL360 Flux |
| Chassis | Streacom Open BenchTable |
Synthetic Benchmark – Ryzen 9 9900X
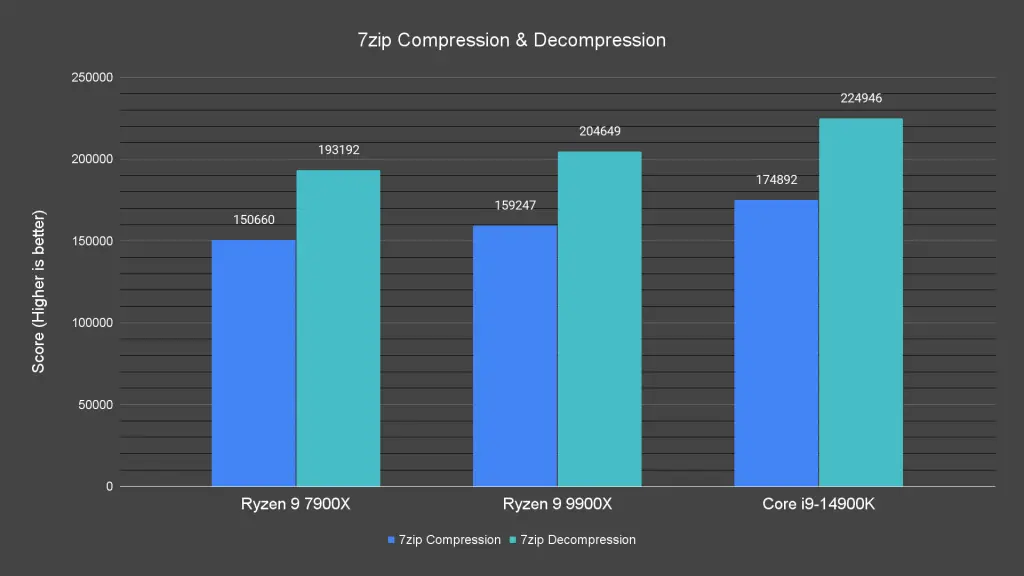
We started by comparing the Ryzen 9 9900X against its predecessor, the Ryzen 9 7900X, and Intel’s Core i9-14900K to assess its performance across various benchmarks. It’s important to note that these results were obtained using a test BIOS provided by AMD on an existing AMD 600 chipset motherboard.
In the 7-Zip compression and decompression benchmark, the Ryzen 9 9900X shows noticeable improvement over the 7900X in both tasks. However, the Core i9-14900K still takes the lead, thanks to its additional efficient cores.
This slideshow requires JavaScript.
When it comes to benchmarks like Cinebench R23, Geekbench 3, SuperPi 32M, and Prime 1024M, the Ryzen 9 9900X excels in single-core performance, often surpassing the Core i9-14900K by a significant margin. This makes it a strong contender for tasks that prioritize single-core power. However, in multi-core benchmarks, the Core i9-14900K maintains an edge due to its efficient cores, offering superior multi-core performance.
This slideshow requires JavaScript.
For creative workloads such as Blender and UL Procyon, the Core i9-14900K continues to shine with its efficient cores, providing a clear advantage in tasks like video editing. However, when tasks rely heavily on main performance cores, the Ryzen 9 9900X holds its ground, sometimes matching the Core i9-14900K. This makes the Ryzen 9 9900X a solid option for creative professionals, depending on the specific demands of their work.
Synthetic Benchmark – Ryzen 9 9950X
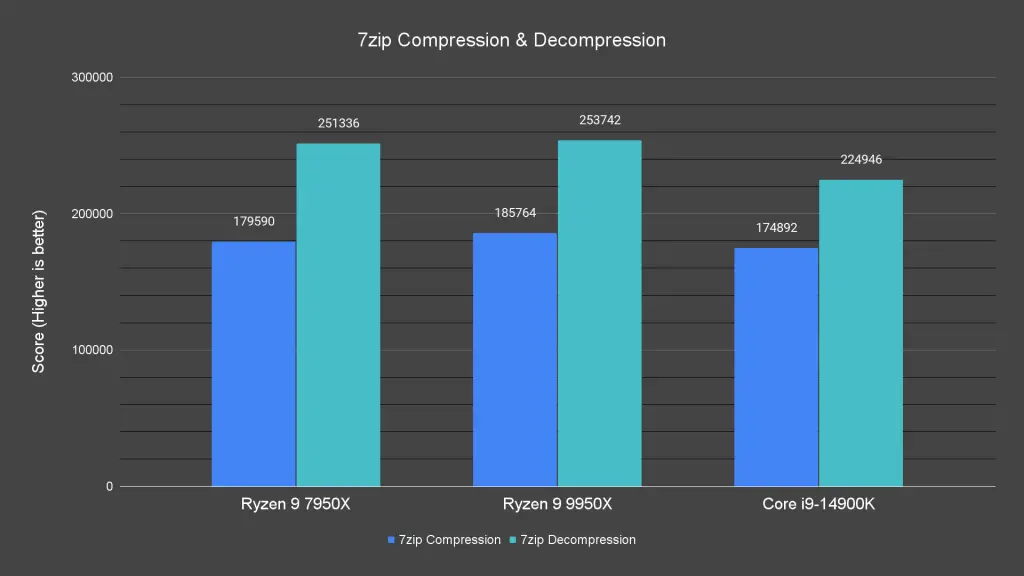
Next, we evaluated the Ryzen 9 9950X, comparing it to the current top-tier CPUs from AMD and Intel, specifically the Ryzen 9 7950X and Core i9-14900K.
In the 7-Zip compression and decompression benchmark, the Ryzen 9 9950X outperformed the 7950X in both tasks, though the margin of victory wasn’t substantial. This indicates that the Ryzen 9 7950X remains a formidable competitor in the high-end desktop CPU market, even a year after its release. On the other hand, the Ryzen 9 9950X clearly outpaced the Core i9-14900K by a significant margin.
This slideshow requires JavaScript.
In benchmarks such as Cinebench R23, Geekbench 3, SuperPi 32M, and Prime 1024M, the Ryzen 9 9950X excels in both single-core and multi-core performance, consistently surpassing the Core i9-14900K by a notable margin, despite the latter’s efficient core advantage over the Ryzen 9 9900X.
This slideshow requires JavaScript.
For creative workloads like Blender and UL Procyon, the Ryzen 9 9950X maintains its dominance. Although the Core i9-14900K showed an advantage over the Ryzen 9 9900X earlier, it couldn’t match the performance of either the Ryzen 9 7950X or 9950X in this round. The Ryzen 9 7950X already demonstrated a clear edge over the Core i9-14900K, but the Ryzen 9 9950X went even further, outperforming both CPUs with ease.
Games Benchmark
In the gaming benchmarks, AMD has improved support for high-frequency memory kits, including DDR5-8000+, with the AGESA 1.1.0.2b update. However, the company still recommends DDR5-6000 as the optimal choice for the Ryzen 9000 series desktop processors.
For our tests, we adhered to AMD’s recommendation by using DDR5-6000 CL30. This setup provides a solid baseline for users who have earlier DDR5 memory kits. Although it’s possible to achieve a 1:1 (UCLK) ratio up to 6400MHz, we prioritized the recommended configuration to ensure consistency and relevance in our results. We plan to explore higher memory frequencies in future tests.
Ryzen 9 9900X Games Benchmark
This slideshow requires JavaScript.
The Ryzen 9 9900X outperformed both the Ryzen 9 7900X and Core i9-14900K in gaming benchmarks, which is expected. While it surpassed its predecessor, the performance gains were less substantial than anticipated, mirroring the results seen with the Ryzen 7 9700X earlier this month – approximately a 5-10% improvement was observed in both cases.
Ryzen 9 9950X Games Benchmark
This slideshow requires JavaScript.
As for the Ryzen 9 9950X, despite expectations of a significant performance lead over the Core i9-14900K, it offers minimal performance gains compared to its predecessor, the Ryzen 9 7950X.
Thermals and power draw
Next, we analyze the thermal and power consumption characteristics of the Ryzen 9 9900X, Ryzen 9 7900X, Ryzen 9 9950X, Ryzen 9 7950X, and Core i9-14900K. To ensure an accurate comparison, all CPUs were tested with unrestricted power limits. The resulting temperature data is summarized in the table below.
| CPU | Power Draw (Idle) | Power Draw (Load) |
| Ryzen 9 9900X | 35W | 162W |
| Ryzen 9 7900X | 36W | 178W |
| Ryzen 9 9950X | 36W | 199W |
| Ryzen 9 7950X | 34W | 225W |
| Core i9-14900K | 15W | 326W |
Under heavy workloads, the Core i9-14900K exhibits significantly higher power consumption compared to both the Ryzen 9 9900X and 9950X. While delivering impressive performance, the Core i9-14900K draws approximately 100W more power than the Ryzen 9 9950X and around 150W more than the Ryzen 9 9900X. This makes the Ryzen 9 9950X the more power-efficient option, offering superior performance while consuming less electricity.
However, the Core i9-14900K demonstrates better idle power efficiency, consuming roughly half the power of the Ryzen 9 CPUs during periods of inactivity.
| CPU | Temperature (Idle) | Temperature (Load) |
| Ryzen 9 9900X | 51°C | 92°C |
| Ryzen 9 7900X | 54°C | 96°C |
| Ryzen 9 9950X | 52°C | 96°C |
| Ryzen 9 7950X | 53°C | 96°C |
| Core i9-14900K | 42°C | 102°C |
Before delving into thermal performance, it’s essential to clarify a common misconception. While manufacturers often assure us that operating temperatures are within safe limits, it’s undeniable that 90°C is a high temperature. It’s crucial to distinguish between “running hot” and “overheating.”
Most modern CPUs employ thermal throttling to prevent overheating and maintain performance. Our testing revealed that Ryzen CPUs consistently operated without triggering thermal throttling. In contrast, the Core i9-14900K reached 102°C on occasion, activating thermal throttling and impacting performance.
Despite these thermal challenges, the Core i9-14900K can still deliver a solid performance under fine-tuned power and load line constraints. The same thing can be achieved with the Ryzen CPUs, especially for those uncomfortable with higher Ryzen temperatures. With the new BIOS update for the AMD 600 series chipset, you can find the newly introduced Curve Shaper feature to fine-tune CPU behavior across different frequency states on top of the existing thermal limit settings.
Ryzen 9 9950X CPU Synthetic Benchmark (Thermal Limit 90°C and Curve Shaper applied)
This slideshow requires JavaScript.
Ryzen 9 9950X Games Benchmark (Thermal Limit 90°C and Curve Shaper applied)
This slideshow requires JavaScript.
Preliminary testing with the Ryzen 9 9950X showcases the potential of the new Curve Shaper feature, coming soon to Ryzen Master. By setting a 90°C load temperature cap and fine-tuning Curve Shaper settings, we achieved notable performance improvements in synthetic benchmarks while reducing overall temperatures. Gaming benchmarks also showed positive results.
Final Thoughts
The Ryzen 9 9900X and 9950X mainly excel in demanding creative workloads, leveraging their multi-core prowess. While both deliver impressive gaming performance, often surpassing the Core i9-14900K, budget-conscious gamers might prefer the Ryzen 7 9700X or Ryzen 5 9600X. For content creators and performance enthusiasts, the Ryzen 9 9900X and 9950X is the optimal choice.
Although not as dramatic as the efficiency gains in the Ryzen 7 9700X, the Ryzen 9 chips still outperform the power-hungry Core i9-14900K while matching or exceeding its performance, demonstrating improved power efficiency over their predecessors with 15-20W less power draw under heavy loads. Our experimental testing with thermal limits and Curve Shaper also revealed significant potential for fine-tuning Ryzen 9000 series CPUs to achieve the optimal balance between power efficiency and performance.
While the Ryzen 9 9950X is a compelling alternative to the Core i9-14900K, especially considering the stability concerns with Intel’s offering, its MSRP of $649 and minimal performance gain over its predecessor aren’t great AMD’s new flagship processor. On the other hand, the Ryzen 9 9900X stands out as a better value at $499 even though it’s still costly, able to offer performance close to the Ryzen 9 7950X with an okay-ish improvement over the Ryzen 9 7900X. It may not be a significant upgrade for current Ryzen 9 7950X or 7900X users, but those upgrading from AMD Zen 3 or Intel 9th-gen Core CPUs will see substantial gains and can experience the benefits of DDR5 over DDR4.